MiR-155-5p inhibits the proliferation and migration of VSMCs and HUVECs in atherosclerosis by targeting AKT1
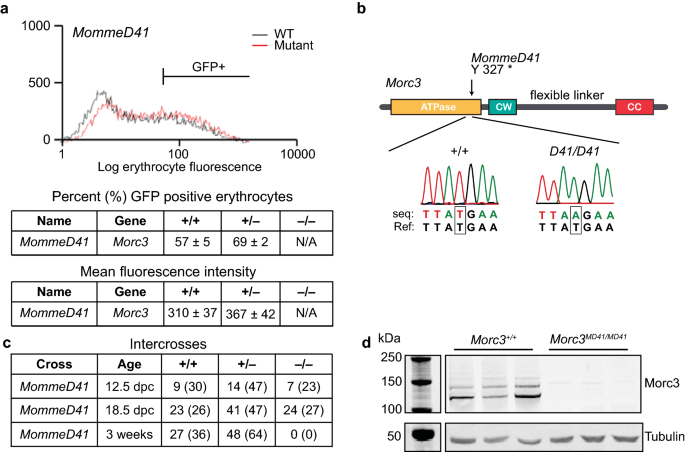
The role of MORC3 in silencing transposable elements in mouse embryonic stem cells | Epigenetics & Chromatin | Full Text
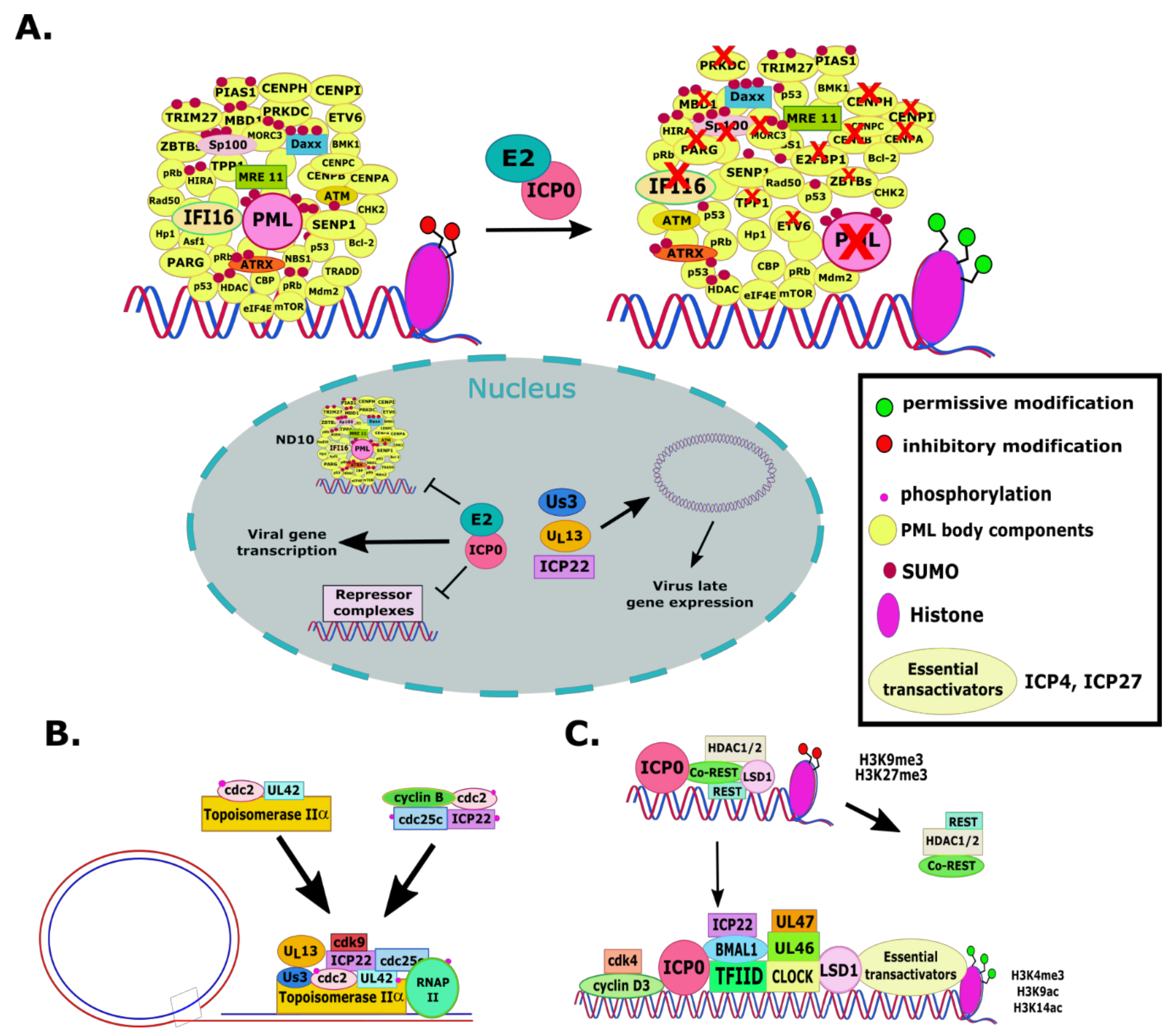
Viruses | Free Full-Text | “Non-Essential” Proteins of HSV-1 with Essential Roles In Vivo: A Comprehensive Review | HTML
Integration of Data from Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation Databases Highlights Concentration and Dosage Sensitivity of LLPS Driv

Morc3 mutant mice exhibit reduced cortical area and thickness, accompanied by altered haematopoietic stem cells niche and bone cell differentiation | Scientific Reports
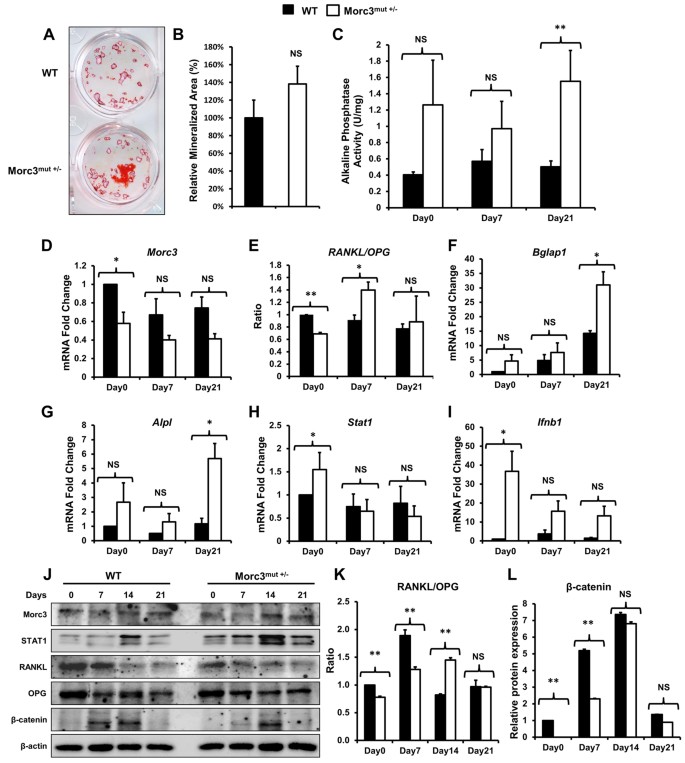
Morc3 mutant mice exhibit reduced cortical area and thickness, accompanied by altered haematopoietic stem cells niche and bone cell differentiation | Scientific Reports

Chemical Biology Approaches to Identify and Profile Interactors of Chromatin Modifications | ACS Chemical Biology
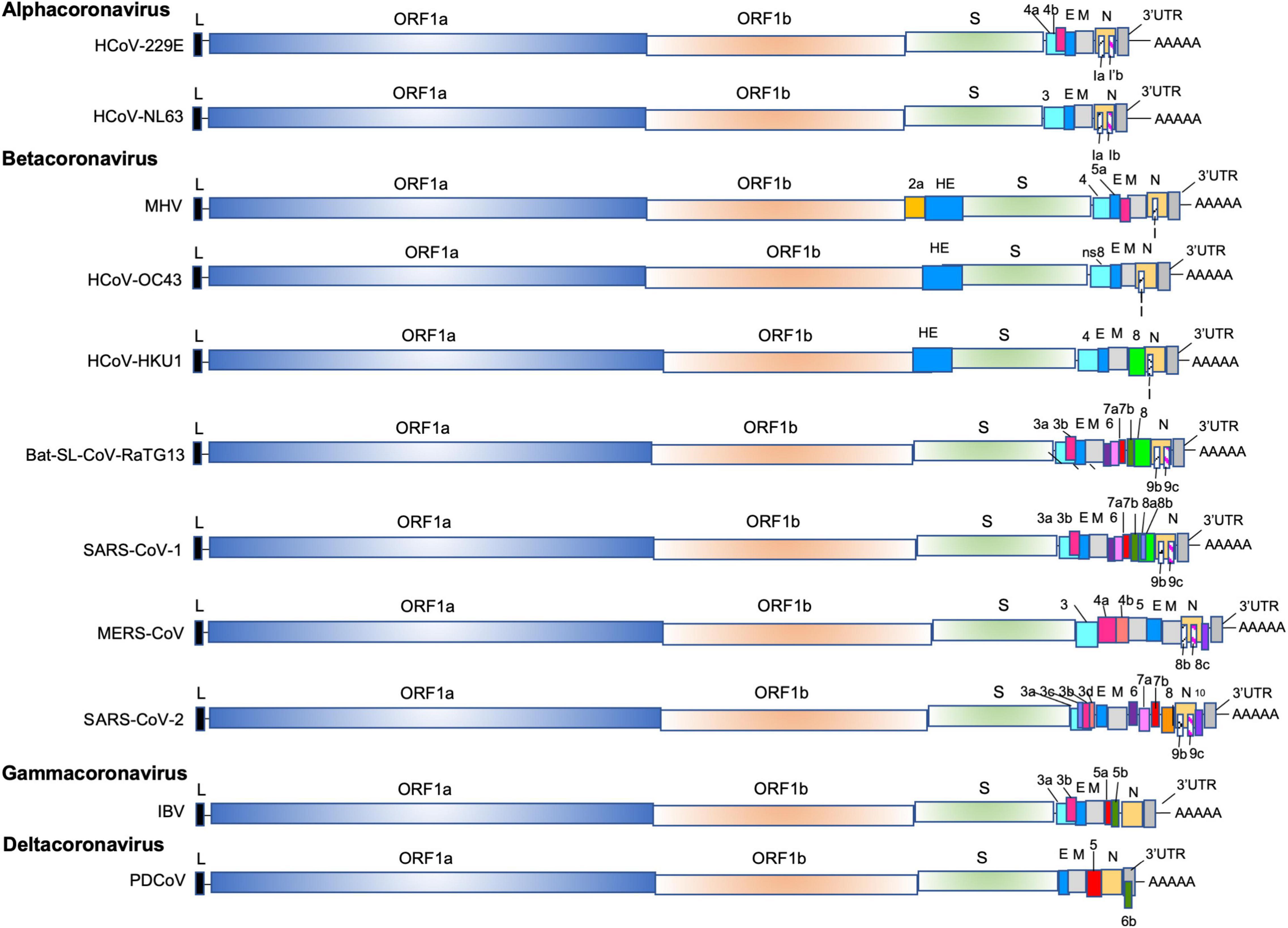
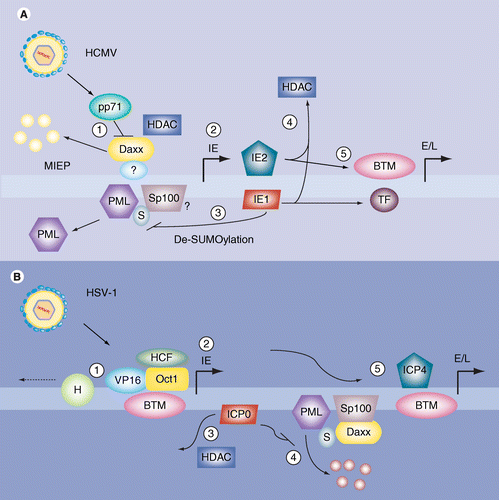
Frontiers | Coronavirus, the King Who Wanted More Than a Crown: From Common to the Highly Pathogenic SARS-CoV-2, Is the Key in the Accessory Genes?
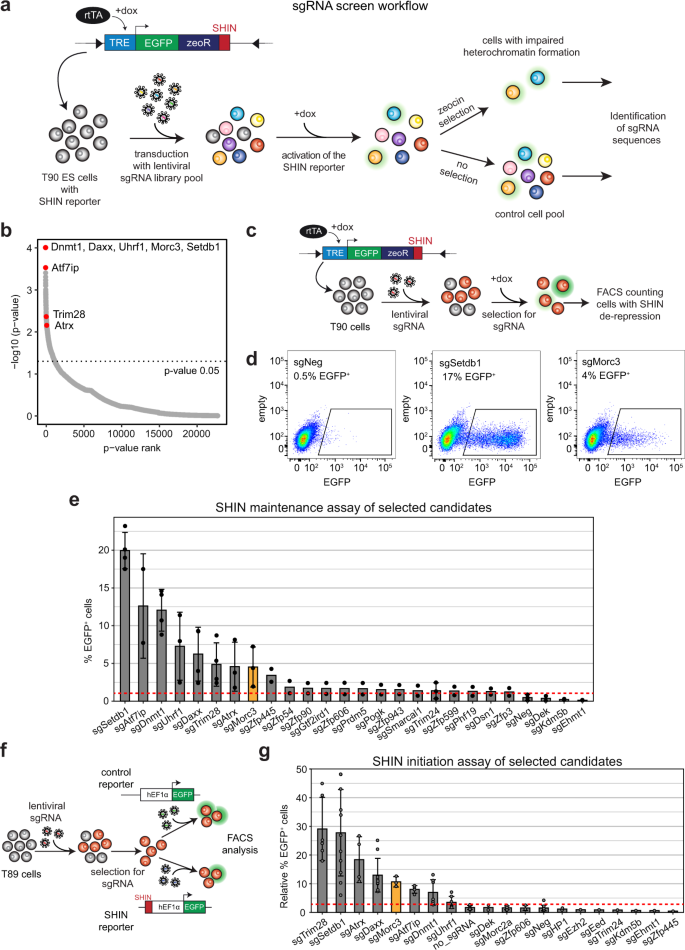
Morc3 silences endogenous retroviruses by enabling Daxx-mediated histone H3.3 incorporation | Nature Communications
Descriptive transcriptome analysis of tendon derived fibroblasts following in-vitro exposure to advanced glycation end products | PLOS ONE

Relationship between DNA methylation and H3K9me3 at ZFP57-binding sites... | Download Scientific Diagram
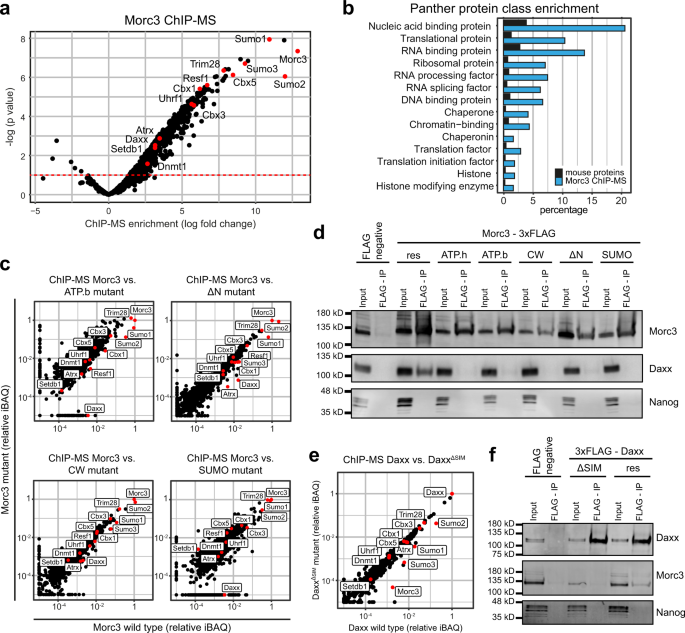
Morc3 silences endogenous retroviruses by enabling Daxx-mediated histone H3.3 incorporation | Nature Communications

Uncovering the mechanistic basis for specific recognition of monomethylated H3K4 by the CW domain of Arabidopsis histone methyltransferase SDG8 - Journal of Biological Chemistry

Binding of the SARS-CoV-2 envelope E protein to human BRD4 is essential for infection - ScienceDirect
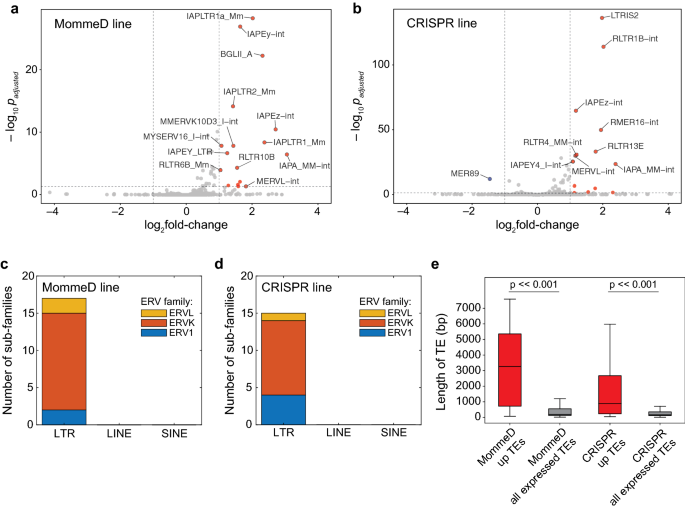
The role of MORC3 in silencing transposable elements in mouse embryonic stem cells | Epigenetics & Chromatin | Full Text
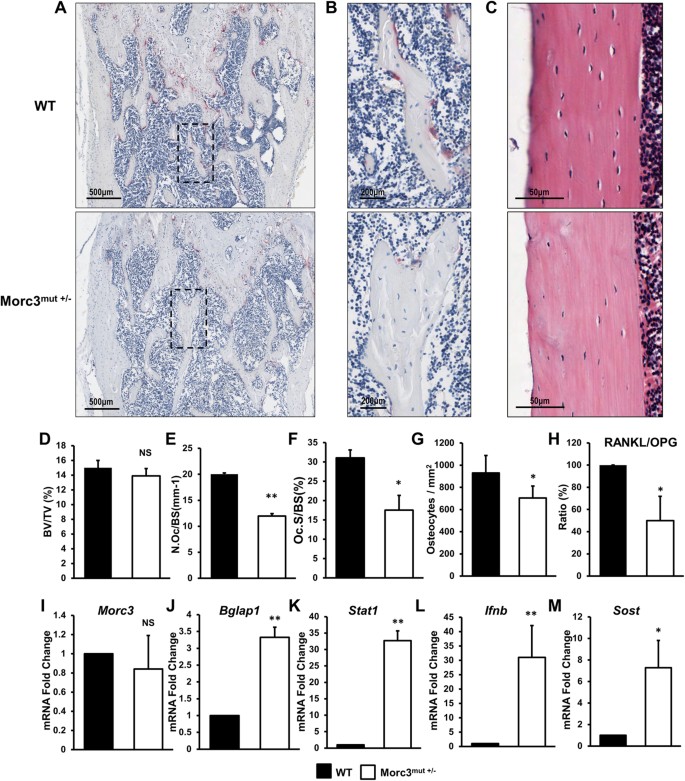
Morc3 mutant mice exhibit reduced cortical area and thickness, accompanied by altered haematopoietic stem cells niche and bone cell differentiation | Scientific Reports